Introduction
The term globalization derives from the word globalize, which refers to the emergence of an international network of economic systems Agenor, (2004). Cowan (2002) noted that Globalization id been used in its economic sense as early as 1981 and in other senses since 1944. Theodore Levitt credited with bringing globalization into the mainstream business in the 1980s (Chortareas, & reodor (2004).
Gobalization is the process of interaction and integration among people, companies’, and governments worldwide Guttal, (2007). Firms consider globalization for capitalist expansion into a global, regulated market economy for example a mobile manufacturer based in Taiwani can manufacture is in several developing countries, ship the parts to another country for assembly, then sell the established mobile to any nation. According to a World Bank (2003) Globalization is a social, cultural, politicnl, and legal phenomenon.
Socially, it leads to greater interaction among various populations
Culturally, globalization represents the exchange of ideas, values, and artistic expression among cultures a trend toward the development of single world culture.
Politically, globalization has shifted attention to intergovernmental organizations like the United Nations (UN) and the World Trade Organization (WTO). *
Legally, globalization has altered how international law is created and enforced.
Historical Background of Globalization
Globalization is a term used to describe the process by which people, cultures, goods, and ideas are becoming increasingly interconnected on a global scale. The roots of globalization can be traced back to ancient times, but the modern era of globalization began in the late 19th century and has continued to the present day.
Here are some key historical events that have contributed to the development of globalization:
- Industrial Revolution: The Industrial Revolution, which began in the late 18th century in Europe and North America, led to the development of new technologies and the expansion of trade and transportation networks. This facilitated the growth of international trade and helped to create a global economy.
- Age of Exploration: Beginning in the 15th century, European explorers began to travel the world, establishing new trade routes and expanding their empires. This led to the exchange of goods, ideas, and cultures across the globe.
- Colonialism: European powers colonized much of the world in the 18th and 19th centuries, which led to the spread of Western culture and values around the world. This also helped to create a global economy as European powers exploited the resources of their colonies.
- World Wars: The two World Wars of the 20th century had a profound impact on the global economy. The destruction caused by the wars led to the creation of international organizations such as the United Nations, the World Bank, and the International Monetary Fund, which played a major role in shaping the post-war global economy.
- Technological Advances: The development of new technologies, such as the internet and air travel, have greatly facilitated the exchange of goods, ideas, and cultures across the globe. This has helped to create a more interconnected and interdependent world.
Drivers of Globalization
- Improved transport
- Improved technology
- Growth of multinational companies.
- Growth of global trading blocks
- Reduced tariff barriers
- Economies of scale leading to increased specialization
- Growth of global media.
- Global trade cycle
- Improved mobility of capital
- Increased mobility of labor
Advantages of Globalization
- Creation of an environment for flow of capital and investment among countries.
- Free flow of technology from one country to another.
- Increase in free flow of goods and services between countries.
- The interdependence between different National stales has increased.
- The communication between people of different countries has increased as a result of revolution in the Global mass media.
- Increased economic prosperity in the developing world.
- Globalization has brought people of different cultures together.
- Free movement of labor among countries.
- Politically and economically, globalization encourages nations to have more international contacts
- Due to globalization, percentage of poverty in developing countries has been reduced and quality of life has also improved.
- Trade initiatives increase cross-border trading by removing supply-side and trade-related constraints.
- Globalization has advanced social justice on an international scale, and advocates report that it has focused attention on human rights worldwide.
- Increased Creativity and Innovation.
- Encourages producers and consumers to benefit from deeper division of labour and economies of scale
- Competitive markets reduce monopoly profits and incentivize businesses to seek cost- reducing innovations
- Gains from the sharing of ideas/skills/technologies across national borders
- Opening up of capital markets allows developing countries to borrow money to over a domestic savings gap
- Competitive pressures of globalization may prompt improved governance and better labour protection
Disadvantages of Globalization
- Economic downturn in one country can create a domino effect through its trade partners,
- Globalization has created a concentration of wealth and power in the hands of small corporate elite which can gobble up smaller competitors around the globe.
- Globalization has also increased homogenization.
- Job Mobility, shipping jobs especially manufacturing jobs, from less developed countries to developing countries.
- Loss of Cultural Identity.
- Globalization has been blamed for the loss of millions of jobs around the world.
- Many multinational corporations have been accused of exploitation when working in poorer.
- Some multinational corporations no longer just limit themselves to corporate activities and become part of politics and actively attempt to influence political decisions in some parts of the world.
- Globalization has potential that intellectual property and designs could be copied and stolen and replicated and sold for cheaper elsewhere,
- Globalization may encourage more offshoring instead of less.
- Globalization benefits the wealthy more than the poor.
Globalization and Competitive Landscape
Rapid changes in techno logy and Globalization has intensified the competitive environment, this has made many entrepreneurs to cope with global markets. Strategic management has always been concerned primarily with the performance of the organization and actions of organization to achieve :ompetitive advantage and create value for customers and its stakeholders. Globalization has resulted n the changing of the competitive landscape, as depicted in the Figure 1.
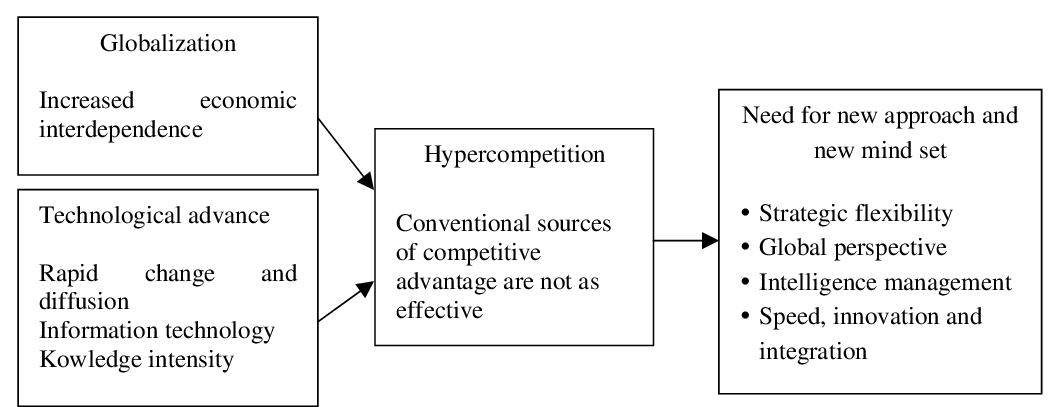
Figure 26.1: Impact of globalization and competitive landscape Source: Kim and Oh (2004)
Figure 1 explains the influence of globalization and technological growth to today’s changing landscape competition and the firm’s strategic actions (Kim & Oh, 2004). There is a need for changes in order to compete intensely in the global economy, the change might be a changing mind set of the term which mean entrepreneurs must be more flexible in their business styles of dealings, managers must take a global perspective in their decision makings and speed, quality and innovation become the yardsticks for customer preference and firm performance (Kim & Oh, 2004).
Strategic Management Model and Porter’s Theory of Competitive Advantage
Wheelen and Hunger i ‘004) provided a model for implementing strategic management which start: from environment scanning, strategic development or formulation to strategic implementation and strategic evaluation. This is depicted in the model below (see Figure 2).
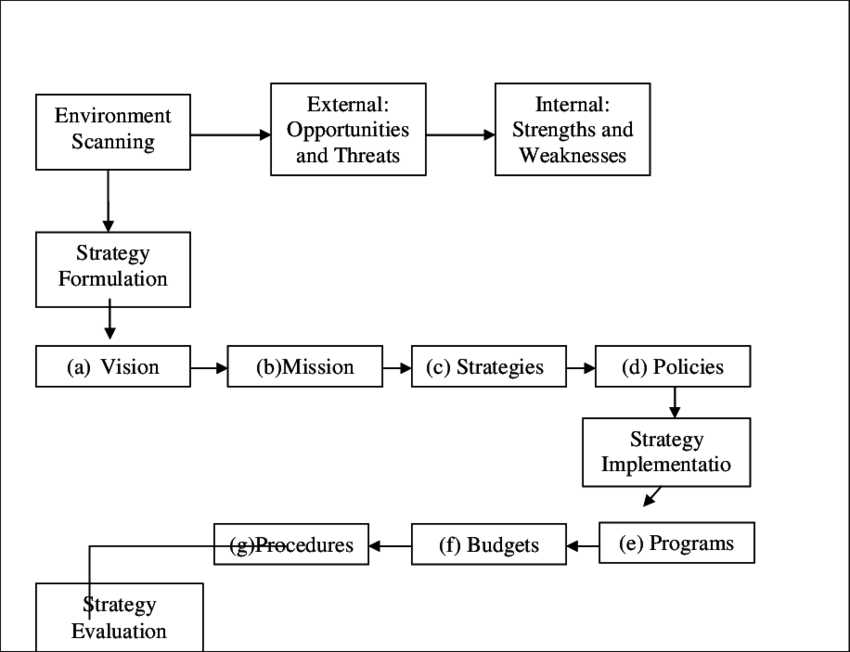
Figure 26.2. Strategic management model by Wheelen and Hunger (2008). Source: Thomas and Hunger (20041
Application of the Model
Wheelen and Hunger (2004) observed that companies do not draw a clear distinction between their domestic and international strategies. However, more and more companies are beginning to extend tile company’s sales, marketing, sourcing, production, human resource and financial strategies beyond national borders. The common phrase heard in the global business now is think global, act local. The justification is to customize products and marketing and sales approaches to the local market. Entrepreneurs or CEOs must constantly discussed global customers, economic trends and markets and help to integrate this information into ongoing strategic management processes in the organization and through business intelligence (Wheelen & Hunger, 2004).
According to Porter (1980) achieving competitive advantage is an important goal of a firm. Porter observed that managers need to identify the sources of competitive advantage of the firm and make, an attempt to identify these sources. For the managers,to achieve this, strategic management provides three different approaches in addressing the issue.
- Porter’s five forces
- The resource based approach
- The relational based approach
