MANAGING HUMAN RESOURCE/ MANAGE HUMAN RESOURCE
1.1. Introduction of the Unit of Learning / Unit of Competency
Human resource management (HRM or HR) is the strategic approach to effectively manage people in an organization in order to unlock their potential to attain a competitive advantage. It is designed to maximize employee performance and efficiency in the unit. It is concerned with the management of people who are the key drivers of any organizational success. HR departments are responsible for overseeing employee-benefits design, training and development employee recruitment, development, performance appraisal and reward management. HR also concerns itself with addressing organizational change and industrial relations arising from collective bargaining and from governmental laws which affect employees. The trainee is expected to analyze the human resource policy in driving functional organizations.
Why Human Resource?
Human Resources plays a key role in an organization as they are responsible for the day to day human resource implementation of the organizational strategies, talent people management, performance review/ management, organizational development and employee motivation. The learner should be able grasp, various management skills, communication, development of policies and procedures which guides the organizational standards and culture. These skills will foster productivity of the human resource and consequent in improve improved performance which will then translate to the organizational success in the long term.
The trainee should be able to demonstrate planning, leadership, effective communication, exhibit analytical skills and critical thinking on area which pertains to HR. The trainee should also be able to undertake human resources inventory for his or her organization for organizational productivity. This can be done through sourcing competent personnel, training and development and motivating the work force.
1.2. Performance Standard
By the end of the training the trainee should be able to develop human resources policy according to organization procedures and changing needs, undertake human resource (HR) planning based on the Strategic Plan, recruit human resource in accordance with human resource Policy and procedures which are in conformity with the constitution and the labor laws.
1.3. Learning Outcomes
- List of Learning Outcomes
- Develop human resource Policy(HR)
- Undertake Human Resource (HR) Planning
- Recruit Human Resource
- Remunerate Human Resource
- Coordinate HR Training and Development
- Carry out Performance Management
- Prepare Performance Improvement Plan
- Develop Functional Managers Teamwork Strategy
- Motivate Organization workforce
- Manage Organization culture and change
- Manage Labor Turnover
- Carry out Succession Planning
- Maintain HR Records
- Prepare Human Resource Annual Report
- Learning Outcome 1. Develop HR Policy
- Learning Activities
| Learning Outcome #No. 1. Develop HR Policy | |
| Learning Activities | Special Instructions |
| · Download an appropriate YouTube video on developing an HR policy, for example, https://www.youtube.com/watch?reload=9&v=fWsLBFN5- mg,
· Draft a compensation and benefits policy for a business organization |
· The facilitator to assist the trainees to download the video provided to guide them to draft a
compensation policy |
- Information Sheet 4/LO 1
Introduction
Human resources policies are critical decision making procedures and regulations which govern the day to day organizational operation and business; they assist in problem solving with the effectiveness in the organizational vision and goal. The Human Resources policies aim at identifying the purpose and objectives which the organization wishes to attain regarding its Human Resources Department. Human Resource policies are developed by making decision and addressing day to day today issues with organization.
Definitions of Key terms
Policy: A policy is a broad guideline for managerial action in implementing objectives. Like a plan, it can be specific and general, abstract and concrete as well as short term and long term. Policies are meant to give direction within organization.
Human Resource Policies: These are broad guideline which explain how objectives are to be achieved and therefore direct the behavior of people in the organization by specifying the range of acceptable behavior.
Policy Management Committee: It’s a group of people who provide ideas or plans that are used by an organization or government as a basis for making decisions
Content
Developing Human Resources Policies
Human Resources are important in any organization as they provide rules and standards through which organizations can function smoothly, they also provide organization with art to design strategy to hand work force.
There are various set procedures that an organization needs to follow in order to come up with to come up with the human resources policies.
Steps for developing Human resources policy
Step 1: Identify the Need for a New Policy.
There are four occasions which require human resources managers to start drafting new policies. New legislation requires organizations to have specific policies in place. New policy is essential to ensure that the organization is in compliance with the law even though legislation does not expressly require one. There’s no consistency in how managers make their decisions which is negatively impacting the workplace. Human resource policy could address issues like work condition and employee relation.
Step 2: Understand What You Want to Achieve with this Policy
Human Resource policies are not only for a chosen few but they cut across the whole organization. By understanding exactly what a policy can achieve you are creating the content and also ensuring that it’s bullet proof.
The following are critical questions to address when determining the need for the Human Resources Polices
- What is the outcome this policy needs to achieve?
- Can it support and promote the desired work culture
- How and by whom will it be monitored and enforced?
- Will it restrict managers from doing their job efficiently? How can this be avoided?
- Will it help the organization attract top talent?
- Will it be easy to implement?
- Will employees welcome it?
- Does it reflect company values? How can it enhance them?
Step 3: Consult with Senior Management
There is probably need approval from senior management before proceeding with the policy, consider consulting them before the policy is written down. This will help ensure that your efforts do not go to waste, while any feedback they have will help you create a better procedure.
It’s important to involve everyone that will be affected by the policy, so there is need to consult with managers who will be responsible for implementing the policies. This will foster ownership of the new policy and hence smoothen implementation.
Step 4: Draft the Policy
As the policy will address employees it’s important to make the language as straightforward as possible. Avoid legal speech and jargon as it’s not necessary, and make sure that the wording is unbiased. It’s also advisable to make the wording as flexible as possible and to allow for exceptions by using terms such as ‘generally’, ‘usually’, ‘typically’ etc.
What to include in a policy.
- The goal of the policy
- The people it addresses to and to whom it applies
- The actual rule or standard you need to communicate
- References such as other policies, documents and legislations that support this policy
- The date the policy comes into effect
Step 5: Review the Policy
Before you start implementing the policy you need to ask the people involved to review it. This will help ensure that people understand the procedure and their feedback can also help you improve the wording of the policy which will be devoid of ambiguity.
It’s always a good idea to put together a group of employees and managers and use them as your test subjects. This will be less time consuming and it will yield the same results as if you were asking everyone in the company.
Step 6: Implementation of the Human Resource Policies.
Once you have gone through the draft HR policies, it is time for implementation. The draft HR policy is approved and implemented according to the organizational procedures and regulations. These helps in the formation of the organizational culture.
(Further reading Kenya Labor Law)
Step 7: Reviewing and revisiting of Human Resource policies.
This is the final step you take in the HR Policies development. Review the policies according to the organizational procedures and changing needs. Reviewing is important it will address the changing needs of the work environment.
The significance of having Human Resource Policies
Human resource policies are significant when addressing, working conditions, compensation and benefits, employee Relation, employee placement, health and Safety and work place diversity. The policies also inform the process of training and Development, Privacy, Sick
Leave, Maternity Leave, Parental and Adoption Leave, Disciplinary Action and Discrimination and Harassment.
Human Resource Polices assists employees to create a framework that will guide their productivity in the organization.
The polices are also viable in giving employees guidelines so that they feel confident and develop a sense of purpose in the organization.
Human Resource Polices assists in risk mitigation and support the organization strategic direction.
An example of Human Recourse policy is a recruitment and selection policy
Elements of recruitment and selecting pokey prices
- Identify the need to recruit
- Decide if to hire internally or externally
- Review the job description
- Select appropriate source
- Decide on the selection stages
- Review resumes in the data base
- Source the candidates
- Shortlist the applicants
- Select the most quality candidates
- Hire the most suitable
- Induct the employee.
- Remunerate and compensate the employee appropriately
Conclusion
Human Resource policies should cover all the human resource functions and should be written and distributed to all employees within the organization. Human Resource Policies can either be written or verbal. Written HR policies can be more authoritative than verbal ones. They serve as valuable aids in orienting and training new employees, in administering disciplinary actions and in resolving grievances and problems among others. You are expected to do further reading on Human Resource policies and explain how they inform the human resource management functions in an attempt to foster organizational competitive advantage.
- Self-Assessment
- Please indicate true or false on the following statements that relate to selection and recruitment policy when hiring.
- It is not important to conduct a needs assessment to determine the manpower requirements (true or false).
- Decides to hire internally or externally is important to foster employee (True or false.
- Please indicate true or false on the following statements that relate to selection and recruitment policy when hiring.
- Selection of employees comes before recruitments (true or false).
- A Short listing applicant not a critical step in the process (true or false).
- State four benefits of Human resource policies in modern
- Describe the steps involved when developing human resource
Practical Exercise
- Visit any two business organization and identify and compare the components of a training and development policy
- Visit any business organization and identify the components of a performance management
- Tools, Equipment, Supplies and Materials for the specific learning outcome
- Writing Materials
- Developed questionnaires
- Tablets
- Computers
- Mobile Phones
- Projectors
- Format templates
- Policy documents
- Sample recruitment template
- Newspaper cuttings on Human Resource Polices
- References
- Career (2019). HR and Recruitment Advice, DQ Media, Ireland.
- Collins (2019). Policy Committee, Dictionary, London.
- Public C. (2016). Human Resource Policies and Procedures, Government Printers Press, Nairobi.
Learning Outcome 2. Undertake Human Resource (HR) Planning
-
- Learning Activities
| Learning Outcome #No. 2. Undertake Human Resource (HR) Planning | |
| Learning Activities | Special Instructions |
| · Visit an organization around your area and assess from the HR records the current human resource inventory.
· Carry out a human resource demand and supply forecast with a relevant business organization using its strategic plan · Visit a business organization and identify the human resource gaps by comparing its current capacity after which you prepare a human resource plan |
· The facilitator should avail the copies of a strategic plan for the students to familiarize |
- Information Sheet 4/LO 2
Introduction
Human resource planning is a process by which an organization moves from its current manpower position to its desired manpower position. It forecasts and or predicts the right number and type of staff that a particular organization will hire, maintain, train, develop and promote per period in line with its strategic objectives.
Definitions of key terms
- Human resource inventory: This is a comprehensive list of all the basic information on all the employees, like their education, experience, skills, age, gender, salary related data, job preference and special achievements.(data bank)
- Demand forecasting: Provides the estimation of the number (quantity) and type (quality) of personnel required. This is done to meet the future personnel requirements of the organization to achieve the desired level of output. Future human resource needs can be estimated with the help of the organization’s current human resource situations and analysis of organizational plans and
- Supply forecasting: Provides the estimation of the available personnel from within and outside the organization. Internal source includes promotion, transfer, job enlargement and enrichment, whereas external sources include recruitment of fresh candidates who are capable of performing well in the organization.
- Strategic plan: A strategic plan is a document that establishes the direction of a company or work
Content
The HR should ensure that the HRP are in relation with the Organizational Strategic Plan. The ideal process of undertaking human resource planning includes the following steps:
- Preparation of a human resource inventory by reviewing the current resource
- Human Resource Policy (HRP) is the continuous process of systematic planning to achieve optimum utilization of an organization most valued assets (Quality of employees it ensures that best fit employees are hired to do the jobs and address manpower
- The inventory is prepared from the application forms filled by the employees at the time of recruitment into the organization
- Conducting a job analysis to come up with a job description and job specification
- Preparation of a human resource forecast to assess the future personnel requirements by determining the demand for a given future time period and preparing an estimate of supply of people who will be available for the selected future
- Comparing the current capabilities of the employees with the future requirements in order to design future program to fill up the gap.
- Undertaking career development programs to prepare management to deal with dynamic and challenging changes that take place over time in organizations and finally
- Formulating the human resource plan to address the deficits or surplus in the organization
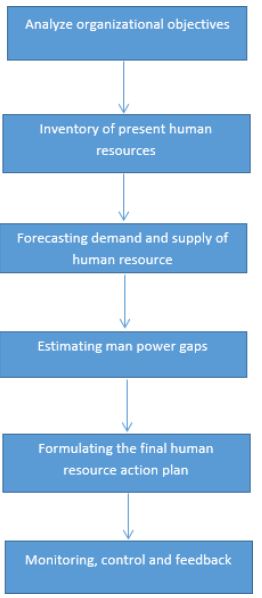
Figure 10: The Human Resource Plan
Factors that Influence Human Resource Planning
Human Resource Policy is influenced by several considerations and key among them are:
- Type and strategy of
- Organization growth cycles and planning
- Environmental uncertainties
- Labour market demands
- Downsizing organization
- Merging organization
- Internal and external
- Social issues and trends
- New technological development
Benefits of Human resource Planning
There are several benefits that are related to effective Human Resource Planning. These include:-
- It makes the organization to receive the desired manpower
- It assists in forecasting the future needs of the
- It fosters better planning for employee development
- Training programs beneath may effective as they den the manpower group
- Assists to make strategies descends related to hiring
Conclusion
An effective Human Resource plan will assist the organization to address the shortages/surpluses, develop plans for recruitment, promotion, retirement or separation, and specify the type of employee to recruit and the type of skill required. Do further readily on the Human Resource Policy process and the limitation of Human resource planning.
The HR planning is a continuous process and the Human Resource managers should always ensure that they have the best resources needed in their firm. Please do further reading on the elements of human resource planning.
Self-Assessment
1. Which among the following is not a factor which influences Human resource planning within an organization?
a) Type and strategy of an organization
b) Organizational growth
c) Labour market demands
d) Environment certainties.
2. Which among the following is a benefit for human resource planning in an organization?
a) Makes the organization to reach the desired man power position.
b) Fostering high employee turnover.
c) Dues not cater for employee training and development.
d) Assists in making poor strategic decides in an organization
3. is the process of forecasting an organizations future demand for, and supply of, the right type of people in the right number.
a. Human Resource Planning
b. Recruitments
c. Human Resource Management
d. Human Capital Management
4. Which of the following factors state the importance of the Human Resource Planning?
a. Creating highly talented personnel
b. International strategies
c. Resistance to change and move
d. All of the above
5. A process that is used for identifying and developing internal people with the potential to fill key business leadership positions in the company is called .
a. Highly talented personnel creation
b. Investing in human resources
c. Succession planning
d. None of the above
6. State true or false
i. Human Resource Planning facilitates international expansion strategies.
a. True
b. False
7. Which of the following option is not the factor that hinders with the human resource planning process?
a. Type and quality of forecasting information
b. Time horizons
c. Environmental uncertainties
d. Unite the perspectives of line and staff managers
8. What is the major issue faced while doing personal planning?
a. Type of information which should be used in making forecasts
b. Types of people to be hired
c. Multiple positions to be filled
d. All of the above
9. Rearrange the following steps involved in the Human resource planning process in proper order.
A. HR Programming
B. HR Demand Forecast
C. Environmental Scanning
D. Control and evaluation of programme
E. Surplus – restricted hiring
F. HRP implementation
G. HR supply forecast
H. Organisational objectives and Policies
I. Shortage – Recruitments and Selection
a. ABCDEFGHI
b. CHBGAFDEI
c. IHDEBCAFG
d. IHGFEDCBA
10. Which of these factors is not included in environmental scanning?
a. Political and legislative issues
b. Economic factors
c. Technological changes
d. None of the above
11. is the process of estimating the quantity and quality of people required to meet future needs of the organisation.
a. Demand forecasting
b. Supply forecasting
c. Environmental forecasting
d. None of the above
12. Which of the below given options are the forecasting techniques used?
A. Ration Trend Analysis
B. Delphi Technique
C. Staffing projections
a. A & C
b. B & C
c. A, B & C
d. A & B
13. Outline the key elements from the following on this link https://urlzs.com/yL3rj on human resource planning.
14. Define the concept Human Resource Planning.
15. Describe the process of undertaking the human resource planning in an organization.
Practical exercise
16. Visit any business organization and assess the current human inventory from the Human Resource records and compare with the strategic plan projections to establish the human resource
Tools, Equipment and Materials
- Writing materials
- Developed questionnaires
- Tablets
- Computers
- Cameras
- Mobile phones
- Projectors
- Format templates
- Human Recourse policy documents
- Organizational inventories
- Samples of manpower establishment for key
4.3.3.5. References
- Saleemi N. A.(1997). Personnel Management Simplified, Nairobi Saleemi Publications, Nairobi
- Learning Outcome 3. Recruit Human Resource
- Learning Activities
| Learning Outcome #No 3 Recruit Human Resource | |
| Learning Activities | Special Instructions |
| · Download the following link https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OJNcYZvToGYand identify the steps in the recruitment process.
· Conduct a role play on an interviewer interviewing an interviewee for a job position in an organization |
· The facilitator to ensure that there is internet connectivity |
- Information Sheet 4/LO 3
Introduction
Recruitment is the process of locating and attracting potential employees to apply for jobs in the organization. It is the searching of qualified candidate who have the relevant skills and expertise to apply for new or an existing job positions. Refers to the overall process of attracting, short listing selecting, apparatus and retaining the best people within an organization.
Definitions of key terms
Employee Placement: It is the process of assigning a new employee to a position within his or her expertise where the employee will have a reasonable chance for success (Dessler, 2008) Employee Induction: It is the process of introducing a new employee to his/her job and organization and giving him all the necessary information required by him/her to start his work. Employee orientation – This is process of facilitation of employees with job environment.
Guidelines for recruiting human resource
- The department heads identify the manpower requirement in accordance with the Human Resource policies. When a section, unit or department has a need for more personnel, the person in charge is supposed to fill in an employee requisition form and send it to the personnel departments
- The recruitment plans are then prepared according to the Human Resource procedures. It is out of the employee requisition that the personnel department can determine whether there are qualified employees within the organization – internal source of recruitment or must be recruited externally – external sources of recruitment
- The advertisement media is then chosen depending on communication procedures used by the organization. Vacant job positions can be filled by the existing personnel (internal recruitment) or by searching outside the organization (external recruitment).
- The online applications and database for applications are set accordance with Human Resource policies and procedures.
- Selection is the process of determining which job applicant fit the jobs. It is the matching of people with the jobs. This is done against set the job description of the advertised post. Selection in many organizations is usually made by line managers
- Interviewing the selected Once the managers get the required qualification from the selection process, they prepare an interview for the qualified candidates to gauge their competency and to ensure the organization get the best.
- Placement Successful candidates are introduced to the organization in accordance with the set rules and procedures. The job description is well explained to them in the process.
- Employee Induction: This is the point at which the employee should be made aware of the nature of the job, the job requirements and the working This fully introduces the new employee to all facets of the job and the organization.
Stages in the recruitment process
Process of recruitment refers to the process of identifying and attracting job seekers in order to create a bar of the qualified job applications.
Effective recruitment programs has the potential to attract large number of qualified applicants who will go through the screening process. The process comprises of the following steps.
- Planning
- Strategy development
- Searching
- Screening
- Evaluation and control Methods for recruitment
This refers to the means by which an organization reaches to the potential job seekers. This also refers to ways of establishing contacts with potential candidates. Some of the methods of recruitment include:
- Direct method
- Indirect method
- Third party
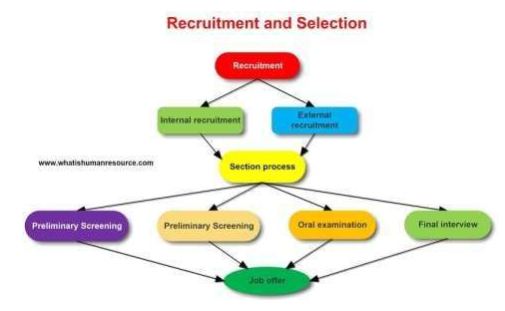
Conclusion
Proper employee recruitment and selection enables an organization to attain its goals effectively and to develop in a dynamic environment. It is important for human resource managers to recruit the right type of people in terms of skills and competencies that are needed to steer the organization to competitive advantages.
- Self-Assessment
- Which of these is the purpose of recruitment?
- Make sure that there is match between cost and benefit
- Help increase the success rate of the selection process by reducing the number of visibly underqualified or over qualified job applicants.
- Help the firm create more culturally diverse work – force
- None of the above
- The poor quality of selection will mean extra cost on and
- Training
- Recruitment
- Work quality
- None of the above
- Which of these is the most important external factor governing recruitments?
- Sons of soil
- Labour market
- Unemployment rate
- Supply and demand
- While recruiting for non – managerial, supervisory and middle – management positions which external factor is of prime importance?
- Political – Legal
- Unemployment rate
- Labour market
- Growth and Expansion
- major internal factor that can determine the success of the recruiting programme is whether or not the company engages in .
- HRP
- Selection
- Induction
- None of the above
- refers to the process of identifying and attracting job seekers so as to build a pool of qualified job
- Selection
- Training
- Recruitments
- Induction
- Give a clear recruitment path followed by a Human Resource manager to ensure they acquire an administrator.
- Describe the process of recruitment when filling a vacancy in an
- Explain any three methods of recruiting in an organization.
- Match the following statements with the correct process as pertains recruitment
- Draft an advertisement to be used to recruit a new employee in a business organization on a relevant post
Tools, Equipment, Supplies and Materials for the specific learning outcome
- Writing materials
- Developed questionnaires
- Tablets
- Computers
- Cameras
- Mobile phones
- Projectors
- Format templates
- Sample recruitment policy
- Copies of job advertisements in the newspaper
- Copy of recruitment guidance and
References
- Dessler, (2008). Human Resource Management. 11th Edition, New Jersey: Pearson Education
- Saleemi A. (1997). Personnel Management Simplified, Nairobi Saleemi Publications, Nairobi.
Learning Outcome 4. Remunerate Human Resource
-
- Learning Activities
| Learning Outcome #No 4 Remunerate Human Resource | |
| Learning Activities | Special Instructions |
| · Prepare a payroll for all employees in a business organization indicating the personnel number, name of employees, basic salary, allowances, compulsory deductions, any voluntary deductions, gross salary and net salary
· Prepare a piece rate pay for 5 casual workers in a printing press x. Note Sorting is 1.50/=, Binding is 1.50/=, trimming is 2.50/= and QC is 0.50/=. Justus bound 200 trimmed 128 books, Monyangaro QC 1340 Books, Ojwang sorted 1420 and QC 120 books, Fred Trimmed 500 books and Martha Sorted 4500 books |
· State the various statutory deductions in Kenya. |
- Information Sheet 4/LO 4
Introduction
Remuneration (Compensation) refers to any payment or reward that an individual receives in return for performing organizational tasks. This is a critical process that has a significant role to play in determining organizational stability. Organizations that remunerate effectively are expected to have competitive advantage over the others. Remuneration provides the basic attraction to employees to return from efficiency.
Definitions of key terms
Remuneration Type: Remuneration packages can be in form of salary, wages, incentives, bonuses, commissions, overtime, medical, housing, transport.
Payroll: It contains a list of all names of individual employees, their personal numbers, gross pay, all deductions both compulsory and voluntary and net pay.
Content
Remuneration of Human Resource
Salaries are paid for services rendered on a monthly basis for regular employment or permanent employees on a yearly basis. Wages are paid for services in accordance with the piece of work done or hours worked.
Bonus is a sum of money given usually at the end of the year or on top of the salary. Usually used mostly by profit making firms. A bonus may be based on contribution to profit, waste reductions, sales increase, and reduction in absenteeism, etc. Most firms supplement a salary with a bonus. A bonus is directly related to results achieved.
Methods of calculating wages and salaries and when they may be used
Flat rate or basic rate – this is a fixed amount of money paid to an employee usually on a monthly basis. It is used to pay salaried workers.
Piece rate – Paid for the completion of given amount of work or unit of product or article. Commonly used for factory workers.
Hourly rate or time rate – time is recorded on a time or clock card and the employee is paid for the number of hours worked in a week or month. It is suitable for employees whose hours of work vary. For example, part time workers.
Overtime – Paid to employees who are required to work extra hours. It is calculated at an agree rate. For example, 1 ¼, 1 and a half, or double the normal rate.
Commission – the worker is paid according to his performance at an agreed percentage. Commonly used in paying sales staff.
Elements of good compensation policy
- Levels and accuracy of wage payment
- Equity in wage payment (equal pay for equal work)
- Recognition of efficiency performance
- Incentive payment
Factors that determine the wages and salaries of employees by an organization
- The firm’s capacity to pay – Those firms enjoying higher profits, higher turnover and higher rate of return over investment can afford to pay higher wages than those firms which are running into losses or enjoying lesser profits.
- Demand and supply of labor at the national, regional, local and organizational levels. If demand for labor is high, the wage rate tends to be high, if the labor supply is scarce, the wage rate would be high
- The existing market wage rate – unless and until a firm maintains the minimum wage offered by the competitors, it cannot retain the labor force because a higher wage rate elsewhere may motivate the labor to step out and join elsewhere where the wage rate is firm supply is scarce, the wage rate would be high.
- The existing market wage rate – unless and until a firm maintains the minimum wage offered by the competitors, it cannot retain the labor force because a higher wage rate elsewhere may motivate the labor to step out and join elsewhere where the wage rate is firm supply is scarce, the wage rate would be high.
- The existing market wage rate – unless and until a firm maintains the minimum wage offered by the competitors, it cannot retain the labor force because a higher wage rate elsewhere may motivate the labor to step out and join elsewhere where the wage rate is To retain, attract, and maintain a sufficient quantity and quality of manpower, a firm should consider the existing wage in the market.
- The cost of living – The wage rate should be based on the increase or decrease in the cost of living When the cost of living increases, workers demand increase in pay. When the cost of living index goes up substantially a revision of wage structure is called for.
- Living wage – This is the wage which should enable the earner to provide for himself and his family not only the basic essentials of food, clothing and shelter but a measure of comfort including education for his children etc.
- Job requirements – Wage structure is based on relative skills required to do the job, efforts needed, responsibility and authority imposed upon and the job conditions.
- Productivity of labor – This is measured in terms of output per man-hour.
- Managerial attitudes – The top management desire to maintain and enhance the company’s prestige has been a major factor in the wage policy of a number of firms.
- Psychological and social factors – Wage equity, fairness and justice are essential in meeting the psychological and social satisfaction to the employees at work.
Methods of wage payment
- Time rate method – It is a convenient method as time spent on the job is measured and wages calculated This is more suitable for such jobs where work cannot be divided into smaller units, for example, the work of an office worker.
- Piece rate method – It provides the employers an easy way of determining labor cost per unit of product. This system ensures fairness by correlating wages and productivity. The inefficient workers are penalized as they get less
Steps in wages system or preparation
- Each employee is given a pay number
- He/She is listed on a payroll (wages book)
- Gross pay is calculated from attendance or work record, depending on whether earnings are paid on a time or piece work
- Gross pay is entered on the payroll together with details of all deductions both voluntary and compulsory
- Net pay is calculated by taking all deductions away from gross pay
- Details of gross pay, personal tax and national insurance deductions are entered on employee tax deduction cards.
- Pay statements (pay slips) are prepared together with pay envelopes.
- A coin and note summary is drawn up to calculate the numbers of notes and different coin required to make up the pay packets.
- The total of net pay is drawn from the bank and individual amounts of notes and coins are placed in pay envelopes.
- Pay envelopes are distributed to employees.
Deductions from gross pay
The rate agreed with an employer (whether calculated on an hourly, weekly or an annual basis) is the gross wage or salary. Before any wages are paid to employees, certain deductions are required to be made by law – otherwise known as Statutory Deductions. Other deductions are agreed by the employee (i.e. they are voluntary) and when all deductions have been totaled and taken away from the gross pay, the remainder (net) is paid to the employee.
Statutory Deductions
These are compulsory deductions authorized by an act of parliament.
- Pay as you earn (PAYE) – It is deducted weekly, or monthly from everyone with a regular income. It is collected by the employer and paid on behalf of employees to income tax department.
- National Social Security Fund – It was established in 1965 through an act of parliament. It is a pension plan or retirement plan where the employees benefit in old age or his family in case he dies before The amount of pension is dependent on the total number of years of service by the employee and the last pay drawn by him. The employee receives his/her pension no longer earning a regular income from employment.
- National Hospital Insurance Fund (NHIF) – It is a health insurance scheme where the employee gets paid for hospitalization It is contributed monthly by an employee. It registers all eligible members from both the formal and informal sector. Formal sector employee’s contributions are deducted and remitted to the funds by their employers. The amount depends on one’s salary.
- Widows and Children Pension Scheme (WCPS) – Under this scheme the Widow and Children receive pension when the bread winner/husband dies if he was a member of this scheme.
Voluntary Deductions
These are deductions made at the request of the employees.
- Insurance – where the employees pays premiums based on the type of policy taken, for example, life, education etc.
- Saving scheme contributions, for example, cooperative society shares
- Trade union dues
- Loan repayments, for example, car loan, bank loan, cooperative loans
- Contribution to social clubs, for example, lions club, Meru sports club
- Mortgage repayments
Net Pay – The net pay is the amount that remains after statutory and voluntary deductions are taken away from the gross pay.
Illustration
Mwanaisha Rajab, Personal No. 7814 is employed by Kwality Services Limited as a clerk is the company secretary department. Her basic salary is Sh. 5,000 as house allowance and Sh.3,000 as medical allowance monthly.
In the course of last month she worked 20 hours overtime at the rate of Sh. 300 per hour. The deduction made from her salary includes PAYE at 10%, NSSF Sh.500, NHIF Sh.400, cooperative shares Sh.500 and loan repayment Sh.1,000. Draw up Mwanaisha’s Rajab pay slip for last month.
KWALITY SERVICES LTD
| Month: January | Personal No: 7814 |
| Name: Mwanaisha Rajab | Department: Company Secretary |
| Job title: Clerk | |
| Kshs | |
| Basic Salary | 15,000 |
| House allowance | 5,000 |
| Medical allowance | 3,000 |
| Overtime | 6,000 |
| Gross Pay | 29,000 |
| Deductions PAYE |
2,900 |
| NSSF | 500 |
| NHIF | 400 |
| Co-operative Shares | 500 |
| Loan Repayments | 1,000 |
| Net Pay | 23,700 |
Payroll/Wages book
The following details relates to employees at Haraka Transporters Ltd
Jane Wairimu payroll number 223, basic salary Sh. 10,000, overtime Sh.3000 Felistas Nekesa payroll number 224 basic salary Sh.15, 000, overtime Nil Isaac Kinyua payroll number 225 basic salary Sh.13, 500, overtime Sh.500
Each employee pays NHIF at Sh.380 per month and PAYE which is calculated at 10% of the Gross earnings.
Prepare a payroll showing their net salaries at the end of the month;
Table 5: Sample of Pay roll
|
Payroll No. |
Name of the Employee |
Gross Pay |
PAYE |
NHIF |
Total Deduction |
Net Pay |
|
223 |
Jane Wairimu |
13,000 |
1,300 |
380 |
1,680 |
11,320 |
|
224 |
FelistasNekesa |
15,000 |
1,500 |
380 |
1,880 |
13,120 |
|
225 |
Isaac Kinyua |
13,500 |
1,350 |
380 |
1,730 |
11,770 |
PAYE = 10% of gross earnings
NET PAY = Gross Pay – Total Deductions
Incentives Schemes
Incentive pay may be regarded as the extra pay that is provided for extra performance in addition to regular pay.
Objectives of using incentive schemes
These include
- Motivate workers to perform effectively
- improve the profit of an enterprise through reduction of the cost of labor and material or both
- To secure a better utilization of manpower/better promotion and performance control
- To increase workers earnings without dragging the firm into a higher wage structure
- To induce effective employees to stick to the enterprise
- To attract effective workers from outside the organization to join the organization
Fringe benefits
Every organization provides some benefits and services to its employees in order to attract and retain them and to maintain loyalty towards the enterprise. Fringe benefits are supplements to wages received by employees at a cost to the employers. The term fringe benefits encompasses a number of benefits such as:
Direct Benefits Profit sharing Co-partnership Sick pay Pension schemes
Health and insurance plan Bonus
Indirect Benefits
Free luncheon vouchers Sports or welfare amenities Provision of a car Telephone
Education for children Canteen
Social facilities
Indirect benefits are aimed at improving morale and increasing the stability of employment.
Why do employers provide fringe benefits to employees?
- Inflation
- When it is not possible for employees to negotiate for higher wages and salaries
- It is a tool of retention if the competitors are using the same Influence of trade unions through collective bargaining
- To highly motivate employees for greater productivity
- Compliance with law and regulations of a country
- To protect the employees against the hazards of life
Conclusion
Organization offer wage or salary that will attract people who can perform the jobs that are available. The offered wage or salary should act as an inducement. Several factors influence the king and amount of pay to be offered namely: external, collective bargaining, job evaluation and the organization policy.
- Self-Assessment
- Explain the concept employees’
- Distinguish between time rate method and piece rate methods of wage payment..
- Which of the following is not an element of a good compensation policy?
- Level and accurate of wage payment
- Incentive payment
- Equity in wage payment.
- Firms’ capacity to
- Which among the following is an indirect benefit among employees in organizations?
- Sick leave
- Free lunch vouchers
- Car prussic
- Social facilities
- Lucy earns a basic salary of Ksh.10, 000. She is paid commission on sales at the following rates:
Sales Value Commission
First Ksh500, 000 4%
Next Ksh500, 000 7%
Sales in excess of Ksh1, 000,000 11%
- During the month of May, Lucy sold goods worth Ksh.1, 600,000. Calculate Lucy’s earnings for the month of May.
- Jack McOtieno is employed in a shoe factory and is paid by piece rate. He is paid Ksh 90 for every pair of shoes he completes to a maximum of 100 pairs. Thereafter, he is paid one and a half times the normal rate for each extra pair he makes. Last month, Jack made 150 pairs of shoes. He contributes Ksh.200 per month for NSSF, Ksh300 per month for Insurance cover and Ksh1, 000 for the Widows and Children Pension
Task Draw up his pay slip for last month’s earnings.
Tools, Equipment, Supplies and Materials for the specific learning outcome
- Writing Materials
- Developed questionnaires
- Tablets
- Computers
- Mobile Phones
- Projectors
- Format templates
References
- Gichira Robert, (1985). A textbook of Office Practice and Organization, Kenya
- Saleemi A. (1997). Personnel Management Simplified,Nairobi Saleemi Publications, Nairobi
Learning Outcome 5. Coordinate HR Training and Development
-
- Learning Activities
| Learning Outcome #No 5Coordinate Human Resources Training and Development | |
| Learning Activities | Special Instructions |
| · Design a training program for a business organization, identifying the steps involved by being guided by this
link.https://evoma.com/business-centre/7-steps-to-create- successful-training-and-development-programs/ |
· The facilitator to ensure the students are online
and have read the attached |
- Information Sheet 4/ LO5
Introduction
Training and development of Human Resources is vital as they are directed towards maintaining and improving current job performance in an organization while programs seek to develop skills for future jobs. Training programs are mainly concerned with the technical aspects of the job and therefore are usually directed at employees. Development programs are mainly for managers. Designing training program by the organizations will assist the employees contribute to the success of their organization and hence meet the organizational goals.
Training and development of Human Resource includes activities such as employee appraisal, training needs assessment, professional development of Human Resource among others..
Definitions of key terms
Employee appraisal-This is a method by which an employee job performance is documented and evaluated generally in terms of quality and quantity, cost and time
Training Needs Assessment-It’s an assessment that looks at employee and organizational knowledge, skills, and abilities to identify any gaps or areas of need
Competence-This is the ability to do something successfully or efficiently.
Professional Development– This is learning to earn or maintain professional credentials such as academic degrees to formal coursework, attending conferences, and informal learning opportunities and put it into practice
Content
Employee appraisal is important as it helps the organization in measuring performance, providing feedback, career planning, performance improvement, management development, compensation changes, and identification of potential for promotion and justification of dismissal/discipline.
Training Needs Assessment
Employees require to be skilled in performing complex tasks in an efficient, cost-effective, and safe manner in the today’s work environment. Training (a performance improvement tool) therefore is needed when employees are not performing up to a certain standard or at an expected level of performance.
Types of Needs Analyses
Many needs assessments are available for use in different employment contexts. The sources that determine which needs analysis is appropriate include: organizational analysis, person analysis, work/task analysis, content analysis, training suitability analysis and cost benefit analysis.
Factors to consider when planning for training and development of employees.
- Nature of the work which employees have been given
- Emergence of new technologies
- New polices that demand for extra training
- Nature of business which employees will wait to venue
- Emerging new market trends
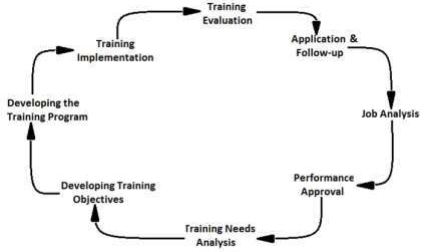
Figure 11: illustration of a Training Cycle
Conclusion
An effective Coordination of HR Training and Development program will depend on employee appraisal, training need assessment, professional development of HR and HR training development
- Self-Assessment
- Which among the following is not a reason to conduct a needs assessment when preparing a training programme for staff?
- To determine the availability of the
- To understand the man power needs
- To discuss areas of weakness among employees
- To inform the nature of the program that will be put into place
- Identify the steps and techniques in training needs analysis after watching the following video on YouTube.
- Download the following you tube on training needs analysis https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=X3cSAjHDeag and Visit a relevant business organization and develop a training program for the workers in the lower level
- Distinguish between training and development as used in Human resource
- Ms Ibrahim have been appointed human resource manager in an organization where employees are redundant and cannot focus in their work
Task
- Conduct a needs assessment to determine cause of reducing and low motivation among
- Prepare an effective training program to address the weaknesses identified to support employees to be more productive.
Tools, Equipment, Supplies and Materials for the specific learning outcome
- Writing Materials
- Developed questionnaires
- Tablets
- Computers
- Mobile Phones
- Projectors
- Format templates
4.3.4.4 References
- NZUVE Management of human resources: A Kenyan perspective.; 1997
- Saleemi A. (1997). Personnel Management Simplified,Nairobi Saleemi Publications, Nairobi
- Learning Outcome 6. Carry out Performance Management
Learning Activities
| Learning Outcome No 6 Carry out Performance Management | |
| Learning Activities | Special
Instructions |
|
· Download the following link and use the sample of a performance development plan https://performancemanager.successfactors.com/doc/po/develop_e mployee/DPsample.html to fill the template on the performance development plan in this link https://performancemanager.successfactors.com/doc/po/develop_e |
Facilitator to assist the students to download |
Information Sheet No. 4/LO6
Introduction
Performance management is based on the principle of management by agreement or contract rather than management by command. It emphasizes development and the initiation of self- managed learning plans as well as the integration of individual and corporate objectives. By the end of this lesson, the trainee should be able to; analyze the concept of Performance Plan, Employee Progress and how to reward employees in order to improve employees’ performance.
Definitions of key terms Performance Plans:
It is a tool to give an employee with performance deficiencies the opportunity to succeed. It may be used to address failures to meet specific job goals or to ameliorate behavior-related concerns.
Operational plans are specific to the daily tasks and requirements to run a business.
Content
Performance Planning Process The cycle is comprised of:-
Performance planning refers to a company’s formal process of identifying
and planning; either an individual’s or an organization’s goals, and the best way to reach them. The planning is done by both the employer and employee through a proper plan called the development plan.
Performance Management: This is an ongoing process of communication between a supervisor and an employee that is progressive throughout the year in support of attaining the strategic objectives of an organization.
This is a cyclic process that varies from to the due to dynamics of organizational objectives
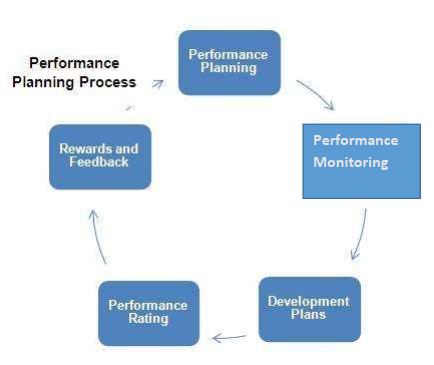
Figure 12: Performance Planning Process
- Performance The supervisor dialogues with the employee and discuss the organizational goals and then they set the target to meet those goals.
- Performance From time to time, both the employer sit down and monitor the change from the set goals or objectives.
- Development Should there be any training needs observed from the employee, and then the supervisor introduces them at this stage.
- Performance After a set period of time, both the employer and the employee go through set stand and check on any deviation. Should there be any positive improvement an employee is rewarded.
- Rewards and There need to be in place proper rewards method and feedback given. Any below the standard performance, employee are encouraged to worker.
In this step the supervision dialogues with employees on the anticipated organizational expectation. This is to ensure employee collaborate on development of the performance objectives.
- Employees development plan are also discussed
- Performance plan is developed that directs employee’s effort towards realization of organizational
- This provides a framework to support employees to attain the self-objectives.
1) Performance monitory
This involves monitory and cheeky employee’s performance against expected objectives. This assists the management to check if the employees are on track to meeting the self- targets. In the event of deviation from self-target appropriate intervention are applied.
Consequently performance will inform the management have the self-process are being adhered to and who is doing what and at what time.
2) Development plans
- This is a flexible tool for assessing improvement of employee’s
- This is used together with performance indicator to identify ways to support employee
- Development plan could also be initiated by employees who are self-driven to meet their
Guide to develop a performance development plan.(steps) Step 1
- Identify area of improvement
- Set experience and outputs Step 2
Outline development goals: Determine if
- Goals are specific
- Is success measurable
- Are the goals realistic
- Will it affect performance
- Is it line with the vision and mission
- Are goals practiced Step 3
- Define development activities
- Outline activity that will assist to achieve set goal Step 4
- Mobilize research needed to complete the activation Step 5
- Before the indication of success and goal accomplishment Step 6
- Analyze what you need form management Step 7
- Define the milestones
3) Performance Refining
This is a work measurement which endures work performance against the self- standards. This could also be performance appraisal to determine the productivity of specific employees in the organization.
4) Rewards and Feedback
Organization must institutes effective reward and feedback mechanisms to be able to motivate the employees to sustain behavior that will lead to goal attainment.
An effective performance measurement uses the following indicators;
Quantity: Indicates how much work is produced. A quantity measure can be expressed as an error rate, such as number one percentage of errors allowable per unit of work, or as a general result to be achieved.
Quality: Outlines how well the work is performed and/or how accurate or how effective the final product is. This must confirm to the expected standards.
Timeliness: I must be within budgeting constraints. The most common error made in setting timeliness standards is to allow no margin for error. As with other standards, timeliness standards should be set realistically in view of other performance requirements and needs of the organization.
Cost-effectiveness: Addresses dollar savings to the organization or working within a budget. Standards should be based on specific resource levels (money, personnel, or time) that generally can be documented and measured in agencies’ annual budget. Cost-effectiveness standards may include such aspects of performance as maintaining or reducing unit costs, reducing the time it takes to produce a product or service, or reducing waste.
Employee commitment: Assessing the ability for employee to show up at work and on time. How it is affecting their work performance and other employees.
Adherence to policy: Addresses deviation from policy and performance goals. Guides the performance.
Professionalism: Addresses how well employees conduct themselves in the work place and comply with dress code/working environment.
NB: The purpose of performance rating is to provide evaluation of the employees’ contribution to the organization
The Performance Improvement Plan (PIP) is designed to facilitate constructive discussion between a staff member and his or her supervisor and to clarify the exact work performance requiring improvement. It is implemented, at the discretion of the manager, when it becomes necessary to help a staff member improve his or her performance. The manager, with input from the affected employee, develops an improvement plan. Click the link https://www.lbwcc.edu/Content/Uploads/lbwcc.edu/files/Performance%20Improvement%20Plan.pdft o read more about the performance improvement plan.
Conclusion
The performance improvement plan is meant to help every employee meet performance expectations against set objectives. Organizations need to use the plan as a tool to help an employee succeed. Use the Performance Improvement Plan when you sincerely believe that an employee is capable of improvement.
Performance Planning Cycle
- Performance planning
In this step the supervision dialogues with employees on the anticipated organizational expectation. This is to ensure employee collaborate on development of the performance objectives.
- Employees development plan are also discussed
- Performance plan is developed that directs employee’s effort towards realization of organizational
- This provides a framework to support employees to attain the self-objectives.
6) Performance monitory
This involves monitory and cheeky employee’s performance against expected objectives. This assists the management to check if the employees are on track to meeting the self- targets. In the event of deviation from self-target appropriate intervention are applied.
Consequently performance will inform the management have the self-process are being adhered to and who is doing what and at what time.
7) Development plans
- This is a flexible tool for assessing improvement of employee’s
- This is used together test performance indicator to identify ways to support employee productivity.
- Development plan could also be initiated by employees who are self-driven to meet their performances.
8) Performance Refining
This is a work measurement which endures work performance against the self- standards. This could also be performance appraisal to determine the productivity of specific employees in the organization.
9) Rewards and Feedback
Organization must institutes effective reward and feedback mechanisms to be able to motivate the employees to sustain behavior that will lead to goal attainment.
Self-Assessment
- If you believe that the employee who needs a formal Performance Improvement Plan (PIP) will never succeed in your organization, this story is for The newly promoted plant manager of a 150-person organization was failing miserably in the key deliverables his boss expected. Communication and performance improvement coaching did not appear to have an impact nor demonstrate that the manager was capable of improving. The manager’s boss, the VP of manufacturing, grew increasingly unhappy with the plant manager’s performance.
- Outline the indicators of an effective performance management
- Explain why it is critical to involve employees when coming up with a development
- Which among the following is not a process in the performance management
- Management process
- Performance monitory
- Effective communication
- Employees rating
- By utilizing the indicators of effective performance management develop sample development plan that meets the set criteria.
- A formal PIP was developed for the plant manager citing eleven goals and their measures of A 90-day time frame was provided as these goals were challenging and not short-term items to accomplish. He was given a strong, supportive environment in which his supervisor’s expectations for his success were a key factor.
Guess what?
He succeeded beyond their wildest dreams. All he needed was serious direction about what he needed to do to succeed.
Armed with the specific direction laid out formally in the PIP, he gathered his whole team, four supervisors and several members of his support staff, and shared the PIP
with its eleven key goals. He asked for their help in reaching the goals so that he (and they) could succeed in the eyes of his boss. They did.
So, watching this process play out made believers of everyone involved in the power of a well-planned, measurable PIP characterized by positive reinforcement and expressed support and encouragement.
From the above case study:
- Demonstrate how the employee was assisted in managing stress which lead to his
- Demonstreate how management of time led to him achieving his
Tools, Equipment, Supplies and Materials
- Writing Materials
- Developed questionnaires
- Tablets
- Computers
- Mobile Phones
- Projectors
- Format templates
References
https://yourbusiness.azcentral.com/operational-goal-7060.html https://www.shrm.org/resourcesandtools/tools-and-samples/how-to- guides/pages/performanceimprovementplan.aspx
Kleingeld: P.A.M (2019) performance management systems: A global perspective, European Journal of work and organization psychology CRC press.
- Learning Outcome 7.Prepare Performance Improvement Plan
Learning Activities
| Learning Outcome No 7 Prepare Performance Improvement Plan | |
| Learning Activities | Special Instructions |
| · Download the following link http://www.publicservice.go.ke/images/guidlines/PSC_37_A_ Final.pdf and prepare a staff appraisal report for any business organization
· Analyze the staff appraisal report and identify the areas of employee improvement |
|
Information Sheet No. 4/LO7
Introduction
A performance appraisal is a regular review of an employee’s job performance and overall contribution to a company. Also known as an “annual review,” “performance review or evaluation,” or “employee appraisal,” a performance appraisal evaluates an employee’s skills, achievements and growth, or lack thereof. Organizations use performance appraisals to give employees feedback on their work performance.
Performance improvement plan is also referred to as- performance actual plan.
It is a management tool that utilizes employee differences and strengths in order to succeed and be able to attain organizational goals.
What is involved in a (PIP) Performance improvement plan?
Critical step
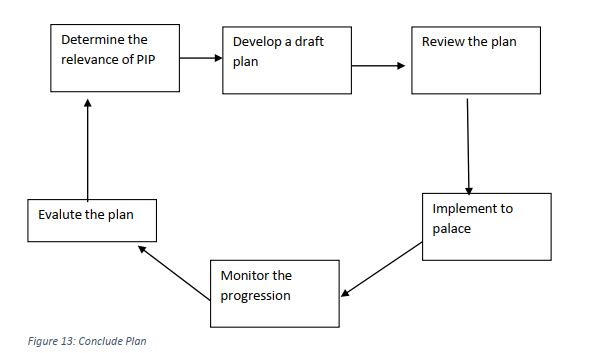
|
|
Figure 13: Conclude Plan
appraisal Reports
These are important to monitor employee productivity. In order to improve employee performance in your organization human resource managers are expected to:
- Communicate clear expectations about the tasks job
- Make sure performance appraisals are consistent to determine the progress
- Make employee development a priority as thus will create a sense of belonging
- Take steps toward improving This will sustain performance.
- Empower employees to do their jobs Offer them skills o do their work through progressive on job training.
- Utilize the right This will support the productive process.
Appraisal preparation
To prepare a performance appraisal, employers are expected to identify the areas of improvement as from the staff reports. They then identify the methods of employee improvements in accordance with the Human Resources policies.
Analyze the simple performance evaluation report.
The budget is very key in the identification of the set appraisal standard. The HR needs to identify the resources available for the same.
Once the performance appraisal is implemented, the HR managers will then carry out monitoring and evaluation. The employer rewards those performers and encourage the below average.

Figure 14: Performance Evaluation Report
Conclusion
Performance appraisals are used to assess an employee’s performance and provide a platform for feedback about past, current, and future performance expectations. Performance appraisal is also called employee rating, employee evaluation, performance review, performance evaluation, or results appraisal. Performance appraisals are widely used for administering wages and salaries, giving performance feedback, and identifying individual employee strengths and weaknesses. Information gathered from the performance improvement plan informs management about employee performance.
Self-Assessment
- Indicate true or false on the following statements on performance appraisal
- Performance appraisal reports inform management decisions
- Performance appraisal mentor employee
- Performance appraisal is not a value based process
- performance appraisal is a collection effort to employees and management
- Visit a business organization in your local area and identify methods of improvement in the performance by the
- Identify the performance improvement resources required to improve the performance by the employees to be able to attain organizational
- Explain the meaning of a performance develop met plan in an organization
- Describe how Human resource managers could conduct performance appraisal in for
Tools, Equipment, Supplies and Materials
- Writing Materials
- Developed questionnaires
- Tablets
- Computers
- Mobile Phones
- Projectors
- Format templates
References
http://www.publicservice.go.ke/images/guidlines/PSC_37_A_Final.pdf https://mitrefinch.com/blog/how-to-improve-employee-performance/ http://www.mnestudies.com/performance-management
Gregory J. (2001) setting performance standards, Concepts methods and Pespectus Lawrence Elbaum associate.
- Learning Outcome 8. Develop Functional Managers Teamwork Strategy
- Learning Activities
| Learning Outcome #No 8 Develop Functional Managers Teamwork Strategy | |
| Learning Activities | Special Instructions |
| · Download the following linkhttps://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DZbmIg0c2s4 and identify the stages in team building. | |
Information Sheet 4/LO8
Introduction
A team is a group of people who collaborate on related tasks toward a common goal. Teams have defined membership (which can be either large or small) and a set of activities to take part in. People on a team collaborate on sets of related tasks that are required to achieve an objective. Each member is responsible for contributing to the team, but the group as a whole is responsible for the team’s success.
Definition of Key Terms
Functional Managers: A functional manager is a person who has authority over an organizational unit—such as a department.
Teamwork Strategy: Strategies that help team members define a collective identity and values they can buy into, and they can employ effective communication and collaboration.
Cross-functional team: It is a group of people with different functional expertise working toward a common goal—and can include people from finance, marketing, operations and human resources.
Teams in the Workplace
Organizations typically have many teams, and an individual is frequently a member of more than one team. Some teams are permanent and are responsible for ongoing activities. In other cases, a team is formed for a temporary purpose.
The Purpose of Teams
Organizations form teams to accomplish tasks that are too large or complex for an individual to complete. Teams are also effective for work that requires different types of skills and expertise.
The primary role of a team is to combine resources, competencies, skills, and bandwidth to achieve organizational objectives. The underlying assumption of a well-functioning team is one of synergy, which is to say that the output of a team will be greater than the sum of each individual’s contribution without a team architecture in place. As a result, teams are usually highly focused groups of employees, with the role of achieving specific tasks to support organizational success.
Different Kinds of Teams
Teams may be permanent or temporary, and team members may come from the same department or different ones. Common types of teams found in organizations include project teams, virtual teams, and cross-functional teams.
- Project teams are created for a defined period of time to achieve a specific goal. Members of a project team often belong to different functional groups and are chosen to participate in the team based on specific skills they can contribute to the Software development is most commonly done by project teams.
- Virtual teams have members located in different places, often geographically dispersed, who come together to achieve a specific
- Cross-functional teams combine people from different areas, such as marketing and engineering, to solve a problem or achieve a goal. Healthcare services are frequently delivered by interdisciplinary teams of nurses, doctors, and other medical
It is common for an organization to have many teams, including teams of several types. Effective teamwork depends on choosing the type of team best suited to the work that needs to be accomplished.
How management can foster that collaboration.
This has been articulated by Susan Heathfield who came up with (12 c) for effective that work and that buildly
- Clear expectation for the performance and expected outcome
- Context: understand the context of
- communication
- control
- Collaboration Creative innovation
- Consequences
- Coordination
- Culture Change
Advantages of Teamwork
The benefits of teamwork include increased efficiency, the ability to focus different minds on the same problem, and mutual support.
The primary benefit of teamwork is that it allows an organization to achieve something that an individual working alone cannot. This advantage arises from several factors, each of which accounts for a different aspect of the overall benefit of teams.
- Higher Quality Outcomes
Teamwork creates outcomes that make better use of resources and produce richer ideas.
- Better Context for Individuals
the social aspect of teamwork provides a superior work experience for team members, which can motivate higher performance.
Challenges to effective team work
Teams face challenges to effective collaboration and achieving their goals.
Individuals Shirking Their Duties, Skewed Influence over Decisions, Lack of Trust, Conflicts Hamper Progress, Lack of Teaming Skills, Missing Task Skills, Stuck in Formation, Too Many Members.
Stages of Team Development
This process of learning to work together effectively is known as team development. Bruce Tuckman, (1965) identified a five-stage development process that most teams follow to become high effective and these are shown in the following diagram.
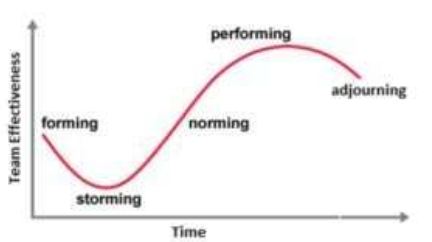
Figure 15: Stages of Team Development
Most high-performing teams go through five stages of team development.
- Forming stage
- Storming stage
- Norming stage
- Performing stage
- Adjourning stage
- Self-Assessment
- Teams occur when a number of people have and recognize that their personal success is dependent on the success of others.
- The same manager
- Similar jobs
- A shared work environment
- A common goal
- Groups which are formed as the consequence of organizational structure and work division are known as:
- informal groups
- formal groups
- target groups
- operational groups
- Distinguish between team and
- Explain four purposes of strong team with organization
- Visit any business organization in your local area and identify how the personnel department collaborates with other departments in the organization to fulfill their task of managing people listing down the benefits of team work in achieving departmental and organizational goals.
- Analyze the five critical stages for effective team development
- By using the 12© by Susan Healtfied link the following statements with the correct
(c) to foster effective team work.
- Instruction passage effectives to the teams(communication)
- Employees work effectively without supervisor ( commitment)
- Each member of the their works a their task ( collaboration)
- Employees therefore their tasks in extra ordinary ways (creativity)
- Leader of the group mention what needs to be done ( control)
- Tools, Equipment, Supplies and Materials
- Writing Materials
- Developed questionnaires
- Tablets
- Computers
- Mobile Phones
- Projectors
- Format templates
- References
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Functional_manager https://courses.lumenlearning.com/boundless-management/chapter/defining-teams-and- teamwork/
- Learning Outcome 9. Motivate Organization Workforce
- Learning Activities
| Learning Outcome #No 9 Motivate Organization Workforce | |
| Learning Activities | Special Instructions |
| · Visit an organization of your choice and identify the financial and non-financial motivators for the employees and give an analysis on which is the most effective
source of motivation and why |
· . |
- Information Sheet 4 /LO 9
Introduction
Motivation may be defined as the complex of forces inspiring a person at work to willingly use his capacities for the accomplishment of certain objectives. It is something that impels a person into action and continues him in action with enthusiasm. Motivates is the willingness to support high level effort towards organizational goals. Motivated employees foster organization productivity and completion advantage.
Content Motivation Types
Intrinsic Motivation
Intrinsic motivation occurs when we act without any obvious external rewards. We simply enjoy an activity or see it as an opportunity to explore, learn, and actualize our potentials.
In work settings, for instance, productivity can be increased by using extrinsic rewards such as a bonus. However, the actual quality of the work performed is influenced by intrinsic factors. If you are doing something that you find rewarding, interesting, and challenging, you are more likely to come up with innovative ideas and creative solutions.
Factors that lead intrinsic motivation.
- Challenge: People are more motivated when they pursue goals with personal meaning and when attaining the goal is possible but not necessarily These goals may also relate to their self-esteem when performance feedback is available.
- Curiosity: Internal motivation is increased when something in the physical environment grabs the individual’s attention (sensory curiosity). It also occurs when something about the activity stimulates the person to want to learn more (cognitive curiosity).
- Control: People want control over themselves and their environments and want to determine what they
- Cooperation and competition: Intrinsic motivation can be increased in situations where people gain satisfaction from helping others. It also applies to cases where they are able to compare their own performance favorably to that of others.
- Recognition: People enjoy having their accomplishment recognized by others, which can increase internal
Extrinsic Motivation
Think about your own motivation for reading this article. Are you trying to learn the material so that you can get a good grade in your Human resource class? This means that you are studying the material to gain external reinforcement (getting a good grade), which means that your behavior is extrinsically motivated.
People who are extrinsically motivated will continue to perform an action even though the task might not be in and of itself rewarding.
Example
A person who works in a manufacturing position, for example, might perform a number of routine tasks that are not enjoyable. Because this person is receiving an extrinsic reward (a paycheck) for completing these tasks, he or she will feel motivated to perform them.
When you want to get someone to do something, such as getting your kids to do their homework, what is the best way to motivate them? Many people might start by offering some type of reward like a special treat or toy. This is a great example of extrinsic motivation since the behavior is motivated by a desire to gain an external reward. Unlike intrinsic motivation, which arises from within the individual, extrinsic motivation is focused purely on outside rewards.
Extrinsic Motivation Can Involve Tangible or Psychological Rewards
Extrinsic motivation is usually defined as our tendency to engage in activities in order to gain some type of known, external reward. It is important to note that these rewards can be either tangible or psychological in nature. Money and trophies are two common types of tangible rewards. People engage in activities that they might normally not find terribly enjoyable or rewarding in order to earn a wage. Athletes often engage in strenuous and difficult training sessions in order to be able to compete in sporting events in order to win trophies and awards.
Extrinsic rewards can be an important tool in motivating behavior, but experts warn that they should be used with caution.
Extrinsic motivation is not a bad thing. External rewards can be useful and effective tool for getting people to stay motivated and on task. This can be particularly important when people need to complete something that they find difficult or uninteresting, such as a tedious work- related project.
Organization Motivation Parameters Financial motivators.
Financial motivators may be in the form of more wages and salaries, bonuses, profit-sharing,
leave with pay medical reimbursements, company paid insurance of any of the other things that may be given to employees for performance. The economists and most managers consider money and financial incentives as important motivators.
Non-Financial motivators.
Non-financial motivators are used to motivate managerial and other higher level personnel.
Employees do not always run after money. They have other needs too. They want status and recognition in the society, they want to satisfy their egoistic needs and they want to achieve something in their lives.
Theories of motivation
Maslow’s Need Hierarchy Theory:
It is probably safe to say that the most well-known theory of motivation is Maslow’s need hierarchy theory Maslow’s theory is based on the human needs.
Figure 16: Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
Herzberg’s Motivation Hygiene Theory:
The psychologist Frederick Herzberg extended the work of Maslow and proposed a new motivation theory popularly known as Herzberg’s Motivation Hygiene (Two-Factor) Theory. (Read more)
McClelland’s Need Theory:
McClelland has identified three basic motivating needs, Viz. Need for Power, Need for Affiliation and Need for Achievement and, along with his associates performed a considerable research work on these basic needs.
Figure 17: McClelland’s Need Theory
McGregor’s Participation Theory:
Douglas McGregor formulated two distinct views of human being based on participation of workers. The first basically negative, labeled Theory X, and the other basically positive, labeled Theory Y.
Theory X is based on the following assumptions:
- People are by nature indolent. That is, they like to work as little as
- People lack ambition, dislike responsibility, and prefer to be directed by
- People are inherently self-centered and indifferent to organizational needs and
- People are generally gullible and not very sharp and
On the contrary, Theory Y assumes that:
- People are not by nature passive or resistant to organizational
- They want to assume
- They want their organization to
- People are capable of directing their own
- They have need for achievement.
Vroom’s Expectancy Theory:
One of the most widely accepted explanations of motivation is offered by Victor Vroom in his Expectancy Theory” It is a cognitive process theory of motivation. The theory is founded on the basic notions that people will be motivated to exert a high level of effort when they believe there are relationships between the effort they put forth, the performance they achieve, and the outcomes/ rewards they receive.
- Self-Assessment
- Download the following link https://www.trackmind.com/idea-generation-vetting- ideas/ and identify the strategies of motivating
- Visit a leading organization, for example, Safaricom mobile company and find out what innovation awards are offered to their employees for innovative ideas and the awards given them.
- Distinguish between intrinsic an extrinsic
- Explain why intrinsic motivation is the best to support employee
- Which among the following is not a theory of motivation
- Mascular
- Expectation
- Theory x and y
- Trait theory
- Assume you are appointed a manager of a teaching marketing organization where productivity has gone down for a period of five
Task:
- explain five ways in which you could motivate the employees to remain forecast on a goal attainment
- what motivation parameters do you think contributed to the performance of the organization going down
Tools, Equipment, Supplies and Materials for the specific learning outcome
- Writing Materials,
- Developed questionnaires,
- Tablets,
- Computers,
- Mobile Phones,
- Projectors
- Format templates
- Sample motivation incentive programs\Chart on the process of motivation
- Materials for role play
References
- Armstron M. & Taylor S. (2014). Armstrong’s Handbook of Human Resource Management 1518 Walnut Street, Suite 1100, Philadelphia PA 19102 USA
- Saleemi A. (1997). Personnel Management Simplified,Nairobi Saleemi Publications, Nairobi
|
|||||||
Learning Outcome No. 10. Manage Organization Culture and Change 3.11.1Learning Activities
- Information Sheet No 4/LO10.
Introduction
An organization’s customs, traditions, rituals, behavioral norms, symbols and general way of doing things are the visible manifestation of its culture; they are what one sees when walking into the organization. The current organizational culture is usually due to factors that have worked well for the organization in the past. Organizations must establish positive cultures for them to succeed
Definition of Key terms
Employee discipline: Employee discipline is defined as the regulations or conditions that are imposed on employees by management in order to either correct or prevent behaviors that are detrimental to an organization.
Change Management process: Change management (sometimes abbreviated as CM) is a collective term for all approaches to prepare, support and help individuals, teams, and organizations in making organizational change.
Organizational Culture: these are the underlying beliefs, assumptions, values and ways of interacting that contributes to the unique social and psychological environment of an organization.
It is way of life of a people and of groups.
Managing Organizational Culture and Change
Change is an individual event, so there are human factors to take into account. That means the more adoption an organization gets from employees, the closer it is to achieving the desired outcomes.
To manage culture change, the first step is to observe and understand your organization’s culture as it is now, and to determine which values will best align with your strategy and structure. Once you decide what your values need to be, design a Cultural Change Plan using the action steps below.
Guidelines: Driving cultural change requires active and intentional leadership. Whether you are changing the culture of a team, a division, or an entire enterprise, use these five steps to manage the process:
- Quantitatively measure your current cultural values. Intentionally align culture, strategy, and .
- Ensure staff and stakeholder participation. (e.g., change sponsor, change committee) that can make timely and clear decisions to prevent an ambiguous vision or delay key
- Communicate and demonstrate the change, again and again and again and then
Content
Be consciously aware of your own mood. If it’s not one that will be useful to your team, change it. Use your nonverbal behaviors to communicate emotional contagion. Make direct eye contact with everyone on the team. Neutralize a negative team member. Create a positive emotional culture within the team.
Clan Culture.
Adhocracy Culture; this is a dynamic and creative working environment.
Market Culture
Leader Type: Hard driver, competitor, producer
Value Drivers: Market share, goal achievement, profitability
Theory of Effectiveness: Aggressively competing and customer focus are effective Quality Improvement Strategy: Measuring client preferences, improving productivity, creating external partnerships, enhancing competiveness, involving customers and suppliers
Hierarchy Culture- This is a formalized and structured work environment. Procedures decide what people do.
Leader Type: Coordinator, monitor, organizer Leadership style and culture:
Look at several leadership and styles available that can define your organization culture,
e.g. Directive, transformational, servant, participative and authoritative leadership styles.
Managing employee grievances
In accordance with the policy guide line and the labor laws of Kenya:
Find a permanent solution; Solve, do not troubleshoot. Your goal should be to come up with a solution that will, as much as possible, put the grievance brought by the employee to rest, rather than provide a temporary fix. Therefore, your goal should be to eliminate the root cause of the problem. Remove the reason for the employee’s complaint.
Listen, and listen well: Remember, all grievances put forth by employees must be heard and listened to the labor laws and the collecting bargain agreement of the organization will guide.
Grievance proceedings should not be allowed to go on for months.
In the same vein, as discussed earlier, once a decision has been arrived at, communicating the decision to the employee should also be done quickly. Do not put it off for later.
How to deal with employee grievance
- Keep an open This means that your objectivity will be shot, and the decision may not be as unbiased as you will later represent it to be.
- Come up with alternative courses of Guided by the organization policy and the labor laws
- Keep all communication lines
- Be responsive whenever the employee reaches out to
- Document every step of the grievance process.
- Establish and implement good policies on handling employee grievance.
- Establish an employee grievances machinery or system in .
- Carrying out employee discipline according to the policy guideline and he labor
NB: It is important for organization to develop a quality management system booklet in accordance with the constitution and labor law for referee to incase of a misconduct and reporting, and the collecting bargain agreement (CBA) of the organization will guide.
Specifically say what defines misconduct, such as theft, assault or battery, insubordination, conflict of interest, recklessness, fraud, breach of confidentiality, drunken and disorderly behavior, falsifying company documents, being under the influence of alcohol or drugs, sleeping on the job, sexual harassment, discrimination and bribery.
The change management Process
The leader should assess the organization’s readiness for change by assessing the organizational culture. Build awareness around the need for change and creating a desire among employees. Therefore, initial communications are typically designed to create awareness around the business reasons for change and the risk of not changing. Likewise, at each step in the process, communications should be designed to share the right messages at the right time.
The following is a diagrammatical representation of a change management process.
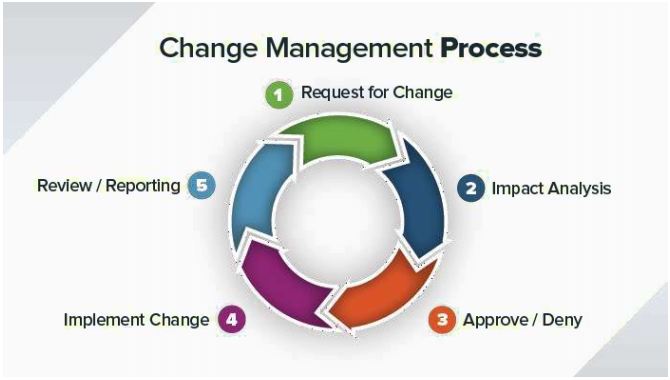
Figure 18: The Change Management Process
Conclusion
The organizational culture has addressed change management, change management process, behavior, and discipline in accordance to HR policy and procedure and reorganization of work culture in accordance of with HR procedures, the constitution and labor laws of Kenya. Labor laws are on the Kenya law website. Do more readily on elements of organization culture and determine its effectiveness in foster organizational productivity.
Self-Assessment
-
- Download the following link https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YEdcJdV2mGc and write down at least five considerations for establishing and maintaining organizational
- Explain the concept of organizational
- Outline the importance of an effective organizational culture.
- Which among the following is not an aspect of organizational
- Beliefs
- Religion
- Dressing
- Policies
- By analyzing the following model of organization culture, explain how a modern organization can be embraced its elements to succeed. The elements are
- History of an organization
- Communication
- Behavior
- Norms
- e) Values
Tools, Equipment, Supplies and Materials
- Writing Materials
- Developed questionnaires,
- Tablets,
- Computers,
- Mobile Phones,
- Projectors,
- Format templates
- Models of change management
References
“Who moved my cheese?” by Dr. Spencer Johnson MD
kenyaemploymentlaw.com
https://www.shrm.org/resourcesandtools/tools-and- samples/toolkits/pages/understandinganddevelopingorganizationalculture.aspx https://study.com/academy/lesson/employee-discipline-in-the-workplace-procedures- principle-quiz.html
Armstrong, M. (2012).Armstrong handbook of Strategic Human Resource Management. London: Kogan
Dessler, G. (2013). Human Resource Management. 13thed. London: Pearson
- Learning Outcome 11. Manage Labor Turn-over
- Learning Activities
| Learning Outcome #No. 11.Manage Labor Turn-over | |
| Learning Activities | Special Instructions |
| · Visit any Business organization and calculate the labour turnover rate of employees using the following formula
Number of employee leaving during a period × 100 Average number employed during a period |
· Use exit interviews or surveys to establish number of employees leaving the organization
· Use human resource inventory records to establish the number of employees employed at a particular period
· Download the link below for guidance on calculation of labour turnover https://www.tutor2u.net/business/referenc e/labour-turnover · |
- Information Sheet No 4/LO11
Introduction
Labor Turnover is the rate of change in the working staff of an organization during a definite period or the proportion of a firm’s workforce that leaves during the course of a year. It’s guided by the organization policy and the labor laws
Definition of Key terms
Labor: Productive activity for the sake of economic gain or the boy of persons engaged in such activity, especially those working for wages.
Turnover: The rate at which employees leave a workforce. Frequency of employee mobility.
Managing Labor Turnover
The organization should make apriority of creating a policy that will curb labor turnover to ensure stability.
Labor is managed in accordance to the HR policy in place in an organization. Determining current labor turnover, establish causes of the same, retention strategies and periodic review of turnover.
Costs or Effects of Labor Turnover
Selection and training costs, Loss of productivity associated with the recruitment, Loss of profit due to loss of production because of training on job, The pay of a learner is in excess of his productivity, unfamiliar with the work give more scrap newbies, rejects and defective work which increase the cost of production, Faulty handling of tools and machinery by workers leading to their breakdown, inexperienced are more prone to accidents leading to loss on account of output, compensation and team spirit due to labor instability, Additional wages in the form of overtime pay have to be paid because of an excessive number of separations causing trouble in meeting contract delivery dates etc.
Causes of labour/employer turnover
These can be classified into several causes e.g. retirement, death, disability, resignation, downsizing/ retrenched etc. That can be categorized in several groups e.g. personal, un- avoidable, reduction/retrenchment.
Case study: www.Kenyalaws.org/casefiles
Conclusion
The labor turnover is determined in accordance with the Human Resource policy and procedures guided by the labor laws and the collective bargaining agreement in case of any in existence.
Labor retention strategies are established in accordance with the Human Resources policies and procedures, periodic review of labor turnover is carried out with policy guidelines.
- Self-Assessment
- Type of turnover which is led in organization by disruptive leaves of employees is considered as
- functional turnover
- dysfunctional turnover
- involuntary turnover
- voluntary turnover
- Absenteeism of employees from job because of funerals in employee’s family or employee’s illness is classified as
- involuntary absenteeism
- voluntary absenteeism
- satisfactory absenteeism
- none of the above
- Type of turnover which is led in organization by disruptive leaves of employees is considered as
- Conduct a research on a particular business organization and identify the reasons why employees are leaving the organization using exit interviews or
- Define the concept labour turnover
- Explain the causes of labour turn over in organization
- What are the implication of high employee from over to organizational stability?
- Outline strategies that organization can undertake to curb employee
- Tools, Equipment, Supplies and Materials
- Writing Materials
- Developed questionnaires
- Tablets
- Computers
- Mobile Phones
- Projectors
- Format templates
- References http://www.publicservice.go.ke/images/guidlines/PSC_37_A_Final.pdf https://www.investopedia.com/what-is-a-performance-appraisal-4586834 http://www.mnestudies.com/performance-management
Hall, L., Taylor, S. and Torrington, D. (2008).Human Resource Management. 7thed. Harlow: Financial Times Prentice Hall.
- Learning Outcome 12. Carry Out Succession Planning
- Learning Activities
| Learning Outcome #No. 12. Carry Out Succession Planning | |
| Learning Activities | Special Instructions |
| · Draw an organization chart to represent an organization structure of a business organization and identify the key positions of the line mangers, functional managers and staff positions. | |
- Information Sheet No 4/ lo 12
Introduction
Succession planning is the process of for identifying and developing teachers who could replace old teachers /mangers when they retire.
Planning/Forecasting the availability of inside executive candidates is very important in succession planning.
Succession planning can be defined as the process of ensuring a suitable supply of successes for current and future, senior or key jobs arising from business strategy so that careers of individuals can be planned and managed to optimize the organization needs and the individual’s aspirations.
Definition of Key terms
Key positions: These are critical positions in an organization where only one person can perform unique duties in an organization, has a specialized knowledge and/or experience acquired over time or through specialized education and training, is a skill rare in the market and is difficult to find qualified candidates despite recruitment efforts, employee will retire within 5 years, departmental heads, position is one of its kind in a particular location or position has external or internal network span both strategically and operationally critical.
Potential employees: The term “Potential” is typically used to suggest that an individual has the qualities (e.g. characteristics, motivation, skills, abilities, experiences etc.) to effectively perform and contribute in broader or different roles in the organization, at some point in the future. Potential is associated with possibilities for the future rather than with problems in current performance.
Succession training strategy: This is a strategy for identifying and developing future leaders at all levels.
Carrying out succession planning
It identifies the key or critical positions that will become vacant within a specified amount of time (typically from 18 months, (one and a half years), to five years), and the competencies necessary to do the work associated with these positions. Its goal is having the right people in the right positions at the right time. The focus of succession planning is on key positions critical to the mission of the organization at all levels.
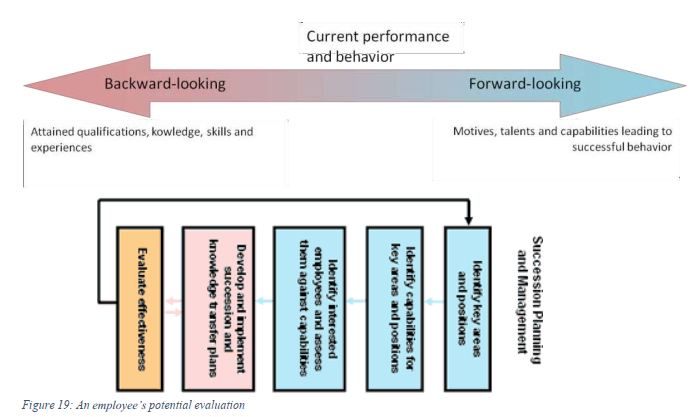
Figure 19: An employee’s potential evaluation
Conclusion/summary
Competencies and profiles of key positions are identified in accordance with the HR policies, potential employees are identified through HR policies succession training strategy on employees is carried out in accordance with HR policy.
Regular review of succession plan is carried out in accordance with the HR policy in place, and development of manuals for senior. Further reading importance of succession planning is encouraged.
Steps to effective successful planning.
- Productiveness of management in dealing with succession plenty
- Having a hope mind so that talent is developed to enable affection
- Market
- Offer regular feedback to upcoming mangers
- Put in place a successful place
- Develop a hiring strategy
- Self-Assessment
- Long term process of identifying plan for replacement of key employees orderly, is classified as
- psychological testing
- performance appraisals
- Long term process of identifying plan for replacement of key employees orderly, is classified as
- assessment centers
- succession planning
- Employee learning concept which states that employees learn best with training if feedback and reinforcement is given is classified as
- massed confirmation
- spaced confirmation
- spatial confirmation
- immediate confirmation
- Which of the following is not a recognized type of plan?
- Business
- Succession
- Ad hoc
- Financial
- Define the concept succession planning
- Explain why organization should have a policy to deal with succession planning
- Outline the factors that could hinder affection succession planning in an
- Download the following linkhttps://www.youtube.com/watch?v=A9h5NlqCSdA on succession planning and identify the factors you consider in getting started for succession
Tools, Equipment, Supplies and Materials for the specific learning outcome
- Writing Materials,
- Developed questionnaires,
- Tablets,
- Computers,
- Mobile Phones,
- Projectors
- Format templates
References
- Armstrong, (2012).Armstrong handbook of Strategic Human Resource Management. London: Kogan
- Dessler, (2013). Human Resource Management. 13thed. London: Pearson
Learning Outcome 13. Maintain HR Records
-
- Learning Activities
| Learning Outcome #No. 13. Maintain HR Records | |
| Learning Activities | Special Instructions |
| · Visit a business organization in your local area and identify the various types of HR
records and ways in which they are managed. |
· Keep an in venture of the records |
- Information Sheet 4/LONo.13
Introduction
Human Resources records includes records covertly employment, position, wages, salary, employee relation, performance management and organizational development.
HR records include the information relating to the human resources of the organization. They are normally too guided by the organization policy and the labor laws. Human resources’ mangers must always keep proper record and update regularly.
Definition of key terms
Records: A thing constituting a piece of evidence about the past, especially an account kept in writing or some other permanent form.
Types of Human Resource Records are: personal, training, health and safety, wages and salaries, leave, performance record and benefits program.
These testimonials are kept in the employee’s personal file. It is the duty of the Human Resource Department to open a file under the employee’s name and also provide him/her with a personal number. It is in this file that all correspondence between the employee and his/her employer will be kept (filed).
At the same time the department completes a Personnel Record Card, containing summarized details relating to you as an employee, may be called employment card. All these are guided by the HR policy and the labor laws.
HUMAN RESOURCE INFORMATION SYSTEMS
Human resource information systems are electronic systems that compile information in databases to be easily accessed and analyzed.
A Human Resource Information System (HRIS), sometimes referred to as Human Resources Management System (HRMS), is software that provides a centralized repository of employee master data that the Human Resource Management (HRM) group needs for completing core human resource (HR) processes be performed and the reporting capabilities make the data stored in the system more accessible and usable.
PURPOSE OF KEEPING PERSONNEL RECORDS
- Helps managers to identify, prepare and implement training programs for employees and executive development
- Facilitates in decision making in respect to giving or refusing transfers, promoting staff, demotion, redeployment etc.
- Helps in preparing wage and salary sheets, and deciding on whether to increase salaries/wages
- Giving reference on employees leaving the organization
- Taking disciplinary action such as suspension or dismissal of staff
- Working out the number of employees, deciding on recruitment of staff, turnover
- To comply with the provisions of various industrial and labour
- Maintains up-to-date information on accidents, absenteeism, labour turnover, leaves, lay-offs, strikes and lock-outs and wage rates prevailing in the organization
- Facilitates human resource audit
NB: Principles of record keeping are: Accountability, Transparency, Integrity, Protection, Compliance, Availability, Retention, and Disposition etc.
HR RECORDS ANALYSIS AND REPORTS
- Traditionally, HR reports have focused upon standard data collection; e. the number of new starters, staff turnover, staff absence rates, employee engagement etc.
- All useful facts of course; yet ‘flat’ and often incomplete data such as this doesn’t create a complete picture – making it difficult to extract useful insights that senior managers can use to aid business
- In contrast, an analytics system allows you to examine, analyze and interpret your data
– telling a story about the true state of the business
Types of HR Analysis Level 1
- Descriptive Analytics. Using descriptive data to illustrate an area of HR, with no analysis
beyond a change over time (known as trend analysis), e.g. turnover statement.
- Descriptive Analytics using multi-dimensional
Level 2
Predictive Analytics. Using data to predict future trends, allowing you to plan for all possible events and scenarios for the good of the business. This can be done, at a basic level, with an Excel spreadsheet and statistical knowledge. Or, via a simple analytics module or system that takes a data feed from your HR system
Level 3
Prescriptive Analytics. This will apply mathematical and computer sciences to suggest options to the data set out in Levels 1 and 2. It will not only predict the outcomes but also the interrelated effects of each decision.
Human Resource analytics software: is used to process raw HR data with the goal to generate valuable insights, improve workplace management, enhance recruitment processes, employee retention, and provide better staffing analysis while saving funds by simplifying HR processes. Human Resources are a big deal in every company. They are people in charge of people, fostering the company’s culture and values to everyone. From recruitment to retention, HR juggle with a lot of different elements that are crucial to assign the right person to the right position.
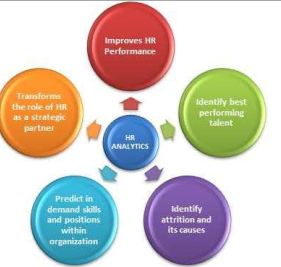
Figure 20: Application of HR Analytics
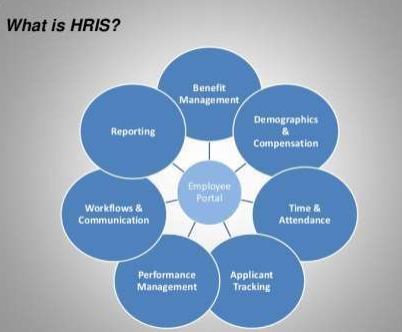
Figure 21: HRIS
Application of HR analytics results in a number of strategic and operational advantages to
HR;
- Increased need for data and analytics tool in HR to make better HR decisions
- Better Quality of Hire is one of the HR data analytics benefits
- A vital benefit of HR metrics and analytics is Employee Retention
- Transformation of HR as a strategic partner is one of the benefits of Workforce analytics
- Business analytics in HR can help predict the hiring needs of an organization
Conclusion
Guided by the organization policy, Records management is the practice of filing, retaining and destroying company records in accordance with government and industry regulations.
Therefore addressing issues on: Obtaining, categorizing, updating, providing, and archiving disposal and security of organization employee records.
The analysis and reports are guided by organization policy and the laws of the country. Further reading and research is encouraged on the importance of Human Resources records.
- Self-Assessment
- .A……………………… is the basic element of data where individual field contains a
single value, such as an employee’s last name, a data or the value of the sensor reading.
- field
- record
- file
- database
- A……………………………. is collection of related fields that can be treated as a unit by
some application program.
- field
- record
- file
- database
- The………………………………. maintains the key characteristic of the sequential file:
Records are organized in sequence based on a key field.
- pile
- sequential file
- indexed sequential file
- indexed file
- The………………………………. retains one limitation of the sequential file: effective
processing is limited to that which is based on a single field of the file.
- pile
- sequential file
- indexed sequential file
- indexed file
- Visit a business organization and identify the security measures implemented to secure their HR records and the guidelines for HR retention policy
- Visit a business organization and identify the various analytical tools related to human resources records to enhance HR decision
- Why is it critical for HR mangers to keep proper HR records?
- Outline solution of the critical records the Human Resources manages are expected to keep
- What is the value of using the HR analytic software to process Human Resource
- Indicate true or false on the following statements describing keeping of Human resources
- Keeping of HR records is a tedious process that is often ignored
- Human resource records could be sued to inform management decision
- Human resource records can assist in recruitment
- Human recourse records called be used to trade employee
- Tools, Equipment, Supplies and Materials
- Writing Materials,
- Developed questionnaires,
- Tablets, Computers,
- Mobile Phones,
- Projectors,
- Format templates
- Sample of some of the Human Resources records
- Date bank containing all the documents for
- References
- Armstrong, M. (2012).Armstrong handbook of Strategic Human Resource Management. London: Kogan
- Dessler, (2013). Human Resource Management. 13thed. London: Pearson
- Learning Outcome 14. Human Resource Annual Report
- Learning Activities
| Learning Outcome #No. 14. Human Resource Annual Report | |
| Learning Activities | Special Instructions |
| · Visit a business organization and identify the standard metrics in Human Capital reporting of the organization.
· To cover the Performance Criteria statements · Trainees to demonstrate knowledge in relation to; The Range in the Occupational Standards and Content in the curriculum |
|
- Information Sheet No 4/LO14
Introduction
An annual HR report is a document where you present all kinds of data and analyses of what how the year has been regarding the company’s human resources policies, the turnover rate, working environment, salaries and compensation. This is important because it can assist to determine if organization objectives were attained or not.
Human Resource Annual Reports
Companies report on a range of human capital metrics through their annual report in order to show how organizations are using this resource to maximum effect.
There are number of Standard metrics that should be reported on. These include:
- Employee numbers
- The composition of the workforce (e.g. analysis by gender, age, full-time or part-time, contingent labor)
- Staff compensation
- Employee benefits entitlement
- Recruitment costs
- Training and development spend (including on health and safety)
- Average hours training per employee category
- Numbers of courses taken
- Reward schemes to align employee behaviors with strategic
- The stability of the workforce (e.g. voluntary and regrettable turnover rates)
- Absence rates: These absences and absenteeism reports
- Talent retention or seniority: Seniority has a very tight relationship with employee motivation and results from a good strategy of talent retention from the
- Average age: This data is especially interesting to know the situation of the company and its staff needs, like what benefits to offer: kindergarten, health insurance, transport,
- Compensation: The average salary offered in the company is really useful to see if the company is competitive enough in the market
- Employee motivation and engagement (e.g. by reference to surveys)
- Retention rates after parental leave
- Internal hire rate
- Accident rates
- Days lost to injury
- Work-related fatalities
- Industrial relations issues
- Revenue per headcount
- Any productivity gains
- Job satisfaction rate = Number of people who report being satisfied ÷ Total number of employees
- Profit per employee = Business profit ÷ Number of employees
- Training spend per employee = Total training costs divided by ÷ Number of employees
- Cost of HR per employee = Total HR salary and benefits ÷ Number of employees
Much human capital reporting currently focuses on inputs and activities, rather than on the outputs and outcomes. It is rare for companies to explicitly demonstrate how their human capital is contributing to value creation.
Critical questions asked should reveal the human capital outcome of either value or risk. All human capital data and information must be ‘material’ in showing “direct, casual connection to value creation (or loss) and decreased (or increased) organization risk.
There are some key reasons to utilize human resources reports during specified time periods, such as monthly and annual:
Identify problem areas, Manage information, HR monitoring, Effective planning, Predictive forecasting and Enhanced communication.
Presenting the data for the annual human resources report
- After gathering all the metrics you must analyze them, make conclusions and take action to improve or maintain the results for the next year. If you are preparing an end of year HR report for the directives of your company all that will help you expose your ideas and show all your efforts are in the right direction.
- Usually the HR department sends a dossier with all the data and graphics to show the people in the general end of year With a PDF it will be enough to show them everything, but you can also print some copies.
A visually engaging way to track vital data, HR dashboards add value by measuring progress, nurturing relationships, and building culture and support: Monitoring and Management:
Regular reporting enables HR to accurately take the pulse of the organization by tracking key workforce metrics.
The Workforce Metrics dashboards provide summary data regarding the current workforce profile, demographic trends, and staff recruitment. The data is refreshed annually.
HR Strategy action plan on HR Capital Reporting;
The action should be modified to better align it with the goals of the Strategic Human Capital Management Plan.HR personnel should decide on a timeline to carry out a strategic HR management review. This review will track the progress made and also identify areas for improvement. The review should be measured against whether changes are helping your company to achieve their goals. Corrective action must be taken if strategic human resource management is failing to meet its objectives.
When reporting, rather than reporting historically, the question should be ‘If I were an investor or owner of this company, what is it that I would want to know about the people side of the business. That is analyzing the people analytics by asking the right questions. Secondly what are the implications of our board of directors, senior executive’s team, HR leaders and outsiders want to know about the people side of the business such as workforce efficiency, effective metrics, and all the information that increases transparency or represent risks the organization needs to monitor, manage and respond to. The HR function and analytics should address these issues.
Functions of a Human Resources Report.
Reporting on the workforce is one of the HR’s essential tasks. When done right, it offers three key benefits for both HR and management:
- HR Regular reporting enables HR to keep a finger on the pulse of the organizations by tracking key workforce metrics.
- Management
- Track problem
- HR reporting pitfalls
- Automate your HR
- Provide relevant information:
- Fix mistakes: HR data is dirty, accuracy is key
- HR reporting and HR dashboards are often a stepping
Conclusion
Human resource monthly/annual report will address: analysis, determine variation from plan, review, strategy and preparation according to organization policy, guided by the laws.
Further reading and research is encouraged
- Self-Assessment
- Visit a business organization and identify the human resource action plans to align variations in the human resource capital reporting with the goals of the strategic human resource management plan.
- Download the following link https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=APhLcYL6QqM on human resource capital reporting and identify what to measure, report and
- Describe the value of any organization keeping the human resource annual reports
- Explain why it is important for Human Resource manages to keep accurate Human resource reports/
- Describe the process of presenting data for the annual human resource reports.
- Tools, Equipment, Supplies and Materials
- Writing Materials,
- Developed questionnaires,
- Tablets, Computers,
- Mobile Phones,
- Projectors,
- Format templates
4.3.12.5 References (APA)
- Armstrong, M. (2012). Armstrong’s handbook of strategic human resource management. London: Kogan
